
Fragrance History
Which were the first known fragrances?
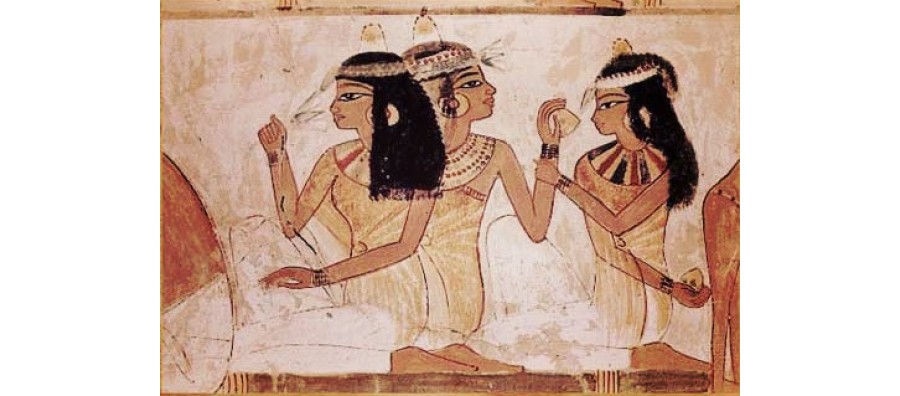
The Egyptians developed aromatic oils and essences 5,000 years ago. Great perfume lovers, they used almond and rose oil, frankincense and myrrh, cedar, mimosa and lily, nutmeg, sweet balsam, cassia, benzoin and labdanum, galbanum and opopanax in such diverse preparations as aphrodisiacs, medicines, cosmetics and incense. In fact, the art of perfumery in Ancient Egypt was so sophisticated that when archaeologists opened Tutankhamen’s tomb in 1922 they discovered an ointment that was still fragrant!
What does ‘perfume’ mean?
The word comes from the Latin, meaning “a sweet-smelling fluid containing the essence of flowers and other substances”. But perfume has its origins in ancient Roman ritual. In the temples of Rome, crushed flowers, leaves, wood shavings, spices and aromatic resins were thrown onto burning coals as offerings to the gods. Their scent was released through smoke ( per fumum).
The study of fragrance, developed in the Nile Valley, was to inspire other ancient cultures. In Greece, athletes anointed their bodies with aromatic oils, and at banquets Romans refreshed themselves between courses with flower-scented water. It was the Persians who developed the use of exotic ingredients and the technique of extracting oils from flowers through distillation. This expertise was brought to Western Europe at the time of the Crusades.

